#73 - Set Matrix Zeroes
Set Matrix Zeroes
- Difficulty: Medium
- Topics: Array, Hash Table, Matrix
- Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/set-matrix-zeroes/
Problem Description
Given an m x n integer matrix matrix, if an element is 0, set its entire row and column to 0’s.
You must do it in place.
Example 1:
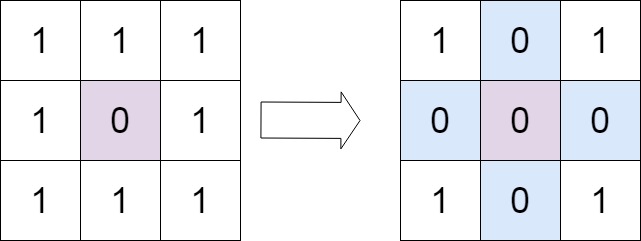
Input: matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Output: [[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]
Example 2:
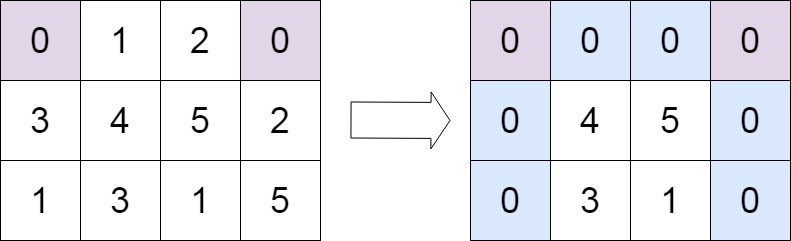
Input: matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]]
Output: [[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[0].length1 <= m, n <= 200-231 <= matrix[i][j] <= 231 - 1
Follow up:
- A straightforward solution using
O(mn)space is probably a bad idea. - A simple improvement uses
O(m + n)space, but still not the best solution. - Could you devise a constant space solution?
Solution
1. Problem Deconstruction
Technical Description: Given an integer matrix , modify in-place such that for every element , all elements in row and column are set to . The transformation must be based on the original state of (newly created zeros should not propagate).
Beginner Description: Imagine a grid of numbers. If you find a zero anywhere in the grid, change every number in that zero’s entire row and column to zero. Do this without making a copy of the grid, and only use the grid’s original state to decide where to place zeros.
Mathematical Description: Define the transformation as:
where , . Compute in-place (overwrite ).
Constraint Analysis:
- : Total elements () allow time but challenge space optimization.
- : Integers cover full 32-bit range, preventing use of special marker values.
- Hidden edge cases:
- Multiple zeros in same row/column (avoid redundant operations).
- Entire matrix is zero (trivial but must handle).
- Zeros only in first row/column (requires separate bookkeeping).
- matrix (no inner cells to process).
2. Intuition Scaffolding
Analogies:
- Real-World Metaphor: Like a contaminated water pipe system where a single polluted junction (zero) taints its entire pipe row and column. Repair crews must map contamination sources without extra blueprints (space).
- Gaming Analogy: In a grid-based RPG, a “curse” tile (zero) spreads to its entire row and column. Players must record curse locations using only the grid itself before activating effects.
- Math Analogy: Compute the union of zero-containing rows and columns. Output is the Cartesian product of these sets projected onto the matrix, requiring efficient set storage.
Common Pitfalls:
- Propagating new zeros: Setting zeros during traversal converts non-zero cells to zeros prematurely, causing exponential propagation (entire matrix becomes zero).
- O(mn) space copy: Storing a full matrix copy violates follow-up constraints.
- O(m+n) space waste: Using separate row/column arrays is better but suboptimal.
- Marker collision: Using integer markers (e.g., -1) conflicts with full-range values.
- First row/column corruption: Using for marking loses critical state if originally.
3. Approach Encyclopedia
Brute Force (O(mn) Space):
- Concept: Copy matrix, scan original, set zeros in copy for every zero’s row/column.
- Pseudocode:
def setZeroes(matrix): copy = [row[:] for row in matrix] # O(mn) space for i in range(len(matrix)): for j in range(len(matrix[0])): if matrix[i][j] == 0: # Based on original for k in range(len(matrix)): # Set column copy[k][j] = 0 for k in range(len(matrix[0])): # Set row copy[i][k] = 0 matrix[:] = copy # Overwrite - Complexity: Time (each zero triggers row+col scan), Space .
- Visualization:
Original: Copy (post-update): [1,1,1] [1,0,1] [1,0,1] => [0,0,0] # After processing (1,1) [1,1,1] [1,0,1]
O(m + n) Space Approach:
- Concept: Store zero flags for rows/columns in separate arrays.
- Pseudocode:
def setZeroes(matrix): m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0]) row_zero = [False] * m # O(m) space col_zero = [False] * n # O(n) space for i in range(m): for j in range(n): if matrix[i][j] == 0: row_zero[i] = True col_zero[j] = True for i in range(m): for j in range(n): if row_zero[i] or col_zero[j]: matrix[i][j] = 0 - Complexity: Time (two passes), Space .
- Visualization:
row_zero = [False, True, False] col_zero = [False, True, False] Matrix becomes: [1,0,1] # row0 unchanged, col1 forced to 0 [0,0,0] # row1 all 0 [1,0,1] # col1 forced to 0
Constant Space (Optimal):
- Concept: Use first row/column as flag arrays. Preserve first row/column zero states in booleans.
- Pseudocode (as implemented):
def setZeroes(matrix): m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0]) first_row_zero = any(matrix[0][j] == 0 for j in range(n)) first_col_zero = any(matrix[i][0] == 0 for i in range(m)) # Mark zeros in inner submatrix (i>=1, j>=1) on first row/col for i in range(1, m): for j in range(1, n): if matrix[i][j] == 0: matrix[i][0] = 0 # Mark row i matrix[0][j] = 0 # Mark column j # Zero inner submatrix based on marks for i in range(1, m): for j in range(1, n): if matrix[i][0] == 0 or matrix[0][j] == 0: matrix[i][j] = 0 # Zero first row/column if needed if first_row_zero: for j in range(n): matrix[0][j] = 0 if first_col_zero: for i in range(m): matrix[i][0] = 0 - Complexity: Time (four passes), Space .
- Visualization (Example 2):
Step 1: first_row_zero = True (M[0,0]=0), first_col_zero = True (M[0,0]=0) Step 2: Mark inner submatrix (no inner zeros → no marks) Step 3: Set inner submatrix: M[1,3]: matrix[0,3]=0 → set to 0 M[2,3]: matrix[0,3]=0 → set to 0 Step 4: Set first row/column: First row → all 0, first column → all 0 Output: [[0,0,0,0], [0,4,5,0], [0,3,1,0]]
4. Code Deep Dive
Optimal Solution (Constant Space):
def setZeroes(matrix):
m = len(matrix)
n = len(matrix[0])
first_row_zero = False
first_col_zero = False
# Check first row for zeros
for j in range(n):
if matrix[0][j] == 0:
first_row_zero = True
break # Line 8: Early exit
# Check first column for zeros
for i in range(m):
if matrix[i][0] == 0:
first_col_zero = True
break # Line 14: Early exit
# Mark rows/columns with zeros (inner submatrix)
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
if matrix[i][j] == 0: # Line 19: Detect zero
matrix[i][0] = 0 # Line 20: Mark row start
matrix[0][j] = 0 # Line 21: Mark column top
# Propagate marks to inner submatrix
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
if matrix[i][0] == 0 or matrix[0][j] == 0: # Line 26: Check mark
matrix[i][j] = 0 # Line 27: Set zero
# Zero first row if flagged
if first_row_zero:
for j in range(n):
matrix[0][j] = 0 # Line 32: Overwrite entire row
# Zero first column if flagged
if first_col_zero:
for i in range(m):
matrix[i][0] = 0 # Line 37: Overwrite entire column
Edge Case Handling:
- Example 1 (No first row/col zeros):
first_row_zero/first_col_zeroremainFalse.- Inner mark: At
(1,1), setmatrix[1][0]=0andmatrix[0][1]=0. - Propagate: Inner cells check marks →
(1,1),(1,2),(2,1)set to 0.
- Example 2 (First row/col zeros):
first_row_zero/first_col_zeroset toTrue.- No inner marks (original zeros at
(0,0),(0,3)not in inner submatrix). - Propagate:
(1,3)/(2,3)set viamatrix[0][3]=0. - First row/column zeroed at end.
- All Zeros:
first_row_zero/first_col_zerobecomeTrue, inner marks irrelevant, entire matrix zeroed in final steps.
5. Complexity War Room
Hardware-Aware Analysis:
- matrix = 40,000 elements → 160KB (4-byte integers).
- Fits in L2/L3 cache (typ. 256KB–8MB), enabling fast passes.
- Four passes ≈ 160,000 operations → <1ms on modern CPUs.
Industry Comparison Table:
| Approach | Time | Space | Readability | Interview Viability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brute Force | 10/10 | ❌ Fails large | ||
| O(m+n) Space | 9/10 | ✅ Good baseline | ||
| Constant Space | 7/10 | ✅ Optimal |
6. Pro Mode Extras
Variants:
- Multiple Transactions (LC 123 Style): “Given operations, each setting a row or column to zero, minimize operations to cover all zeros.” Reduces to bipartite vertex cover (NP-hard for arbitrary ).
- Persistent Zeros: “Zeros must persist across timesteps; new zeros propagate recursively” → requires BFS/DFS (not in-place).
Interview Cheat Sheet:
- First Mention: “This runs in time with space by repurposing the first row/column.”
- Critical Checks: “Did you account for first row/column corruption? Store their states first.”
- Test Cases: Always test:
- Zero at .
- Zero in first row only.
- Zero in inner submatrix only.
- All zeros.